Difference between revisions of "Infotainment System"
Steve Cable (Talk | contribs) |
Steve Cable (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
At it's core, the Infotainment System can be logically broken down into three parts: the host script, the audio handler(s), and display/input pages. | At it's core, the Infotainment System can be logically broken down into three parts: the host script, the audio handler(s), and display/input pages. | ||
| − | = Host script = | + | === Host script === |
This is blah blah | This is blah blah | ||
Revision as of 22:21, 23 May 2019
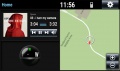
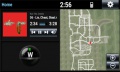
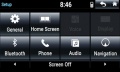
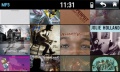
Applications include infotainment systems and instrument panel displays. The standard system available with miniSim models a typical OEM infotainment system including the following functionality:
- Radio (requires internet connection)
- MP3 playback
- Navigation (NADS Springfield map only)
- Platform Independent (iOS, Android, Windows, Raspberry Pi)
Architecture
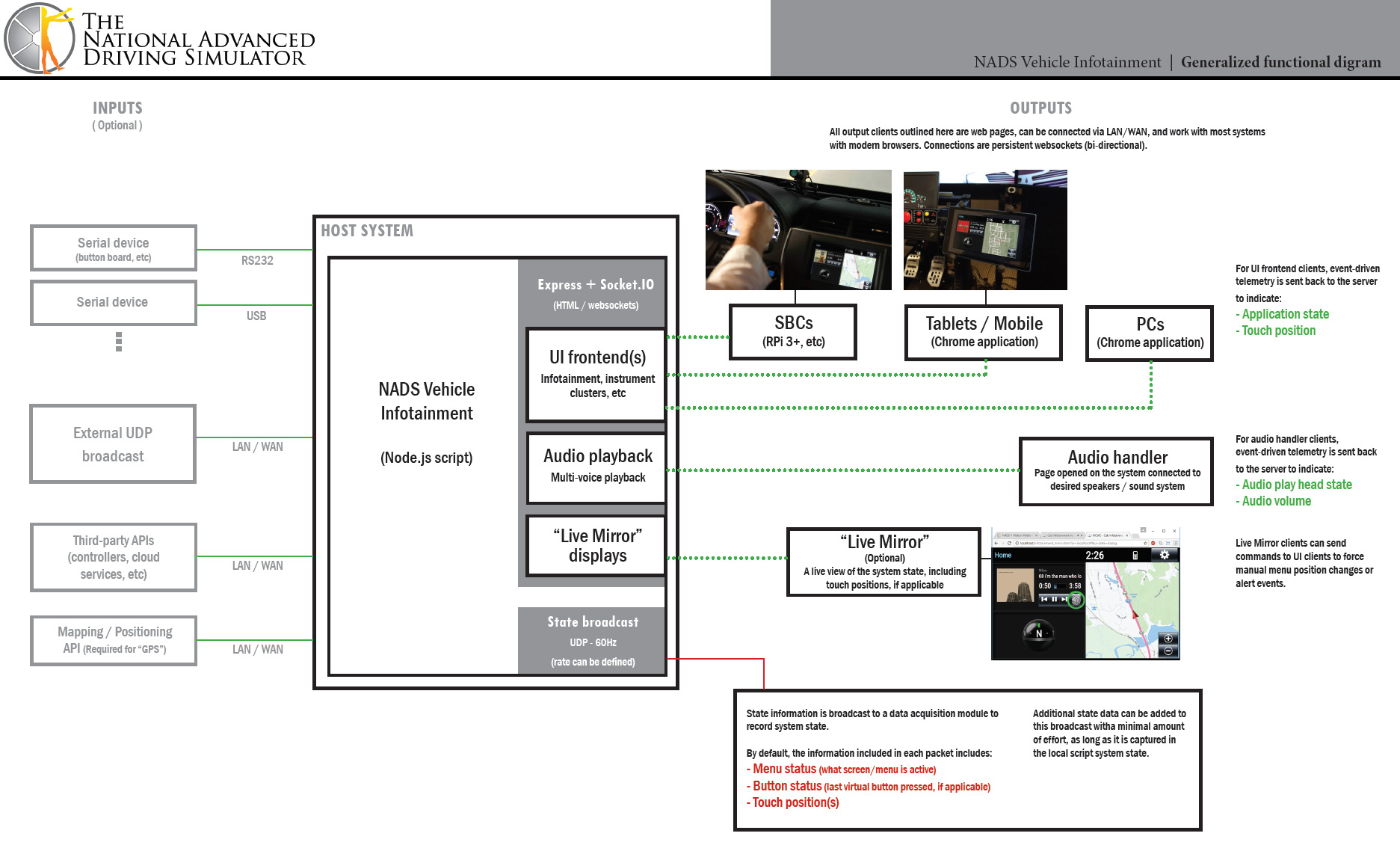
At it's core, the Infotainment System can be logically broken down into three parts: the host script, the audio handler(s), and display/input pages.
Host script
This is blah blah