Difference between revisions of "Vehicle Automation"
Steve Cable (Talk | contribs) |
Steve Cable (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:va_minisim_flow_diag1.jpg|700px|thumb|center]] | ||
Revision as of 13:39, 7 January 2018
As standard, the miniSim is equipped with two automation functions:
- Lane Following
- This function allows the user to define a ‘path’ for the own-vehicle vehicle during scenario authoring in ISAT, and, when engaged, the own-vehicle will follow this path. Lane Follow can be engaged/disengaged manually by the driver or operator, or via scenario trigger. NBy default, this will disengage when the driver starts steering.
- Enhanced ACC
- This function allows the driver or scenario to set the desired target speed and follow distance. The system will accelerate the own-vehicle from a standstill, and brake it to a stop as in stop and go traffic.
The Vehicle Automation option provides additional support for the following miniSim functions that allow the user to create and test automated vehicle control algorithms.
- Virtual World API
- This is a programmer interface for the miniSim logical road network, or ‘virtual world’. Using this interface, a user’s system can query the scenario determine the location of scenario objects, road and lane locations, and the status of traffic control devices.
- Vehicle Automation Option
- The NADS team have developed a set of low-level behaviors that can be activated by the scenario, by manual action, or by a user-designed external subsystem. There are also functions for transfer of control, high-level driving style parameters, and support for existing scenario control triggering systems.
- User-Defined Simulator Subsystem
- The minSim supports linking to user-defined subsystems. The ability to link user developed functions to the subsystem has many applications, including the incorporation of active vehicle safety systems or automation functions into the miniSim driver in the loop simulation environment.
Logical Database API
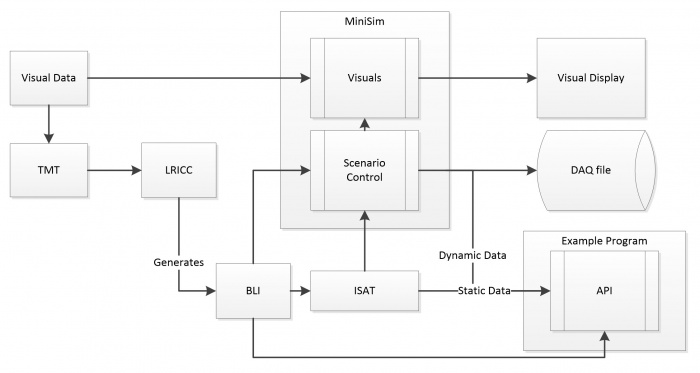
This Logical Database API is to provide a simplified programmer interface into CVED, to serve as a method to extract road information at run time on the MiniSim. This API will not directly serve as an interface into the MiniSim, it will however be able to open the BLI file and run parallel with the MiniSim. As part of the delivery an example program that does provide a communication interface to the MiniSim, and utilizes this API will be delivered. The below figure shows the data-flow, where the example program receives the current state information including the position of the driver, the example program then uses this information to query the API.
Definitions:
| CVED | Correlated Virtual Environment Database is an API used internally at NADS to read the bli, and query the road network. |
| BLI | Binary Logical road Interface, this is a file that contains all of the logical road information. |
| SOL | The sol file provides static information about static or dynamic objects, such as the bounding box size. |
| Corridor | A corridor is a defined path through an intersection. |
| Static Object | Static objects include signs, and non-moving objects that are either part of the BLI, or inserted into ISAT by the scenario author. |
| Dynamic Object | Dynamic objects are those objects that when created by running the scenario, have a physical presence in the simulation, and are updated by scenario control. These are either ADOs or DDOs. |