Difference between revisions of "Infotainment System - Technical Overview"
Steve Cable (Talk | contribs) (→Output (UDP stream)) |
Steve Cable (Talk | contribs) (→Display/input pages) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
:These are the first three types | :These are the first three types | ||
| − | === | + | === Skins === |
<html> | <html> | ||
<div style="width:42%; float:right; margin:0 0 1em 1em;"> | <div style="width:42%; float:right; margin:0 0 1em 1em;"> | ||
Revision as of 21:45, 24 May 2019
Contents
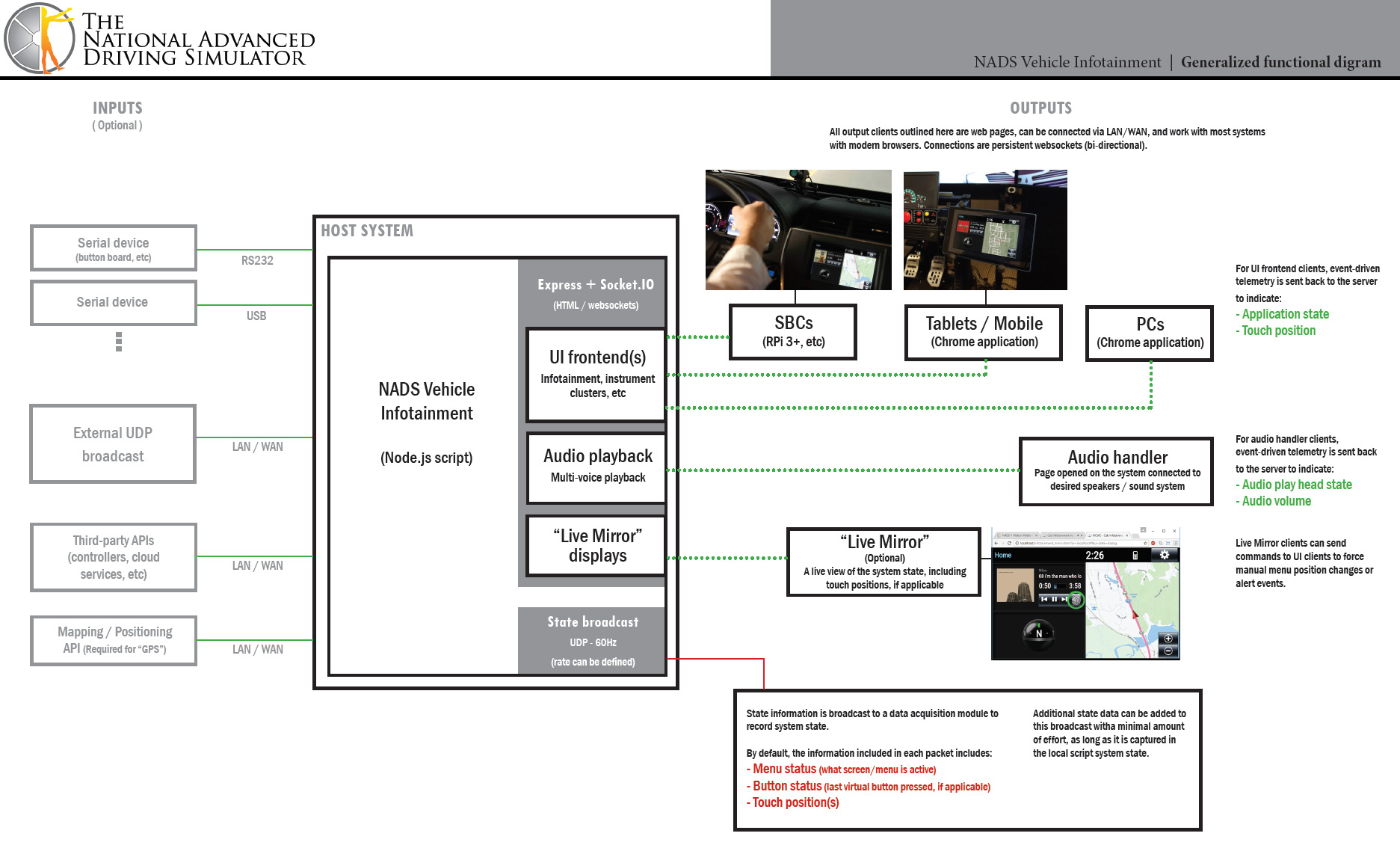
Architecture
The core of the Infotainment system is written in Node.js. It establishes an Express web server, then uses Socket.IO to manage connections to different control and/or display surfaces. Because display, audio and control surfaces are coded as web pages served up by the Express server, the Infotainment system creates a device-agnostic ecosystem, where any number of devices on any combination of platforms can participate (assuming they support a semi-modern browser).
In general, the Infotainment System can be logically broken down into three parts: the host script, the audio handler(s), and display/input pages.
Host script
- The host script operates as the beating heart of the Infotainment system. It manages the services for the display/input interface pages, listens to variable stream information from a miniSim, coordinates interface input, and broadcasts system state data back to the miniSim.
- For it's real time interface to a miniSim, the Infotainment system leverages the Route Table to supply miniSim variable data streams (speed, position, ...) as well as write it's own back to the miniSim's shared memory.
Audio handler(s)
- By default, a single audio page (infotainment_audio.htm) is included. This page can handle 3 channels of stereo playback:
- Media playback
- Alert (temporarily mutes media playback on play)
- Notify
- These are the first three types
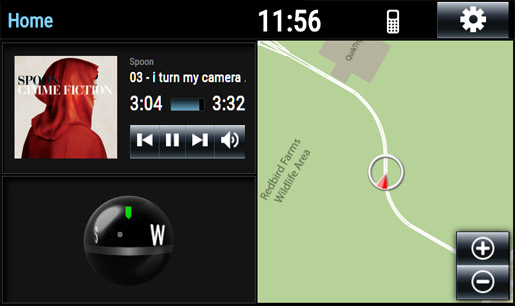
Skins
- Individual web pages serve up visual interfaces/control surfaces, depending on the desired output. This includes (but is by no means limited to):
- Standard OEM-like infotainment interfaces
- Reconfigurable instrument cluster displays
- General touch and/or voice interfaces
- Head-up displays (HUDs)
- "Alert" devices
- By default, the Infotainment System includes an interface for an approximation of the Toyota Entune center stack system (main infotainment and researcher "mirror").
Input (UDP stream)
Output (UDP stream)
The host script outputs a UDP stream to an IP and port defined in the infotainment_config.txt file in the root directory of the Infotainment System install. By default, four variables are shared from the infotainment system and fed back into the miniSim's shared memory:
- AUX_Info_Screen (1 short)
- AUX_Info_Button (1 short)
- AUX_Info_Cursor (2 shorts)
- AUX_MID_Screen (1 short)